Humanization
Graft human germline regions onto an entry to humanize the sequence.
Method
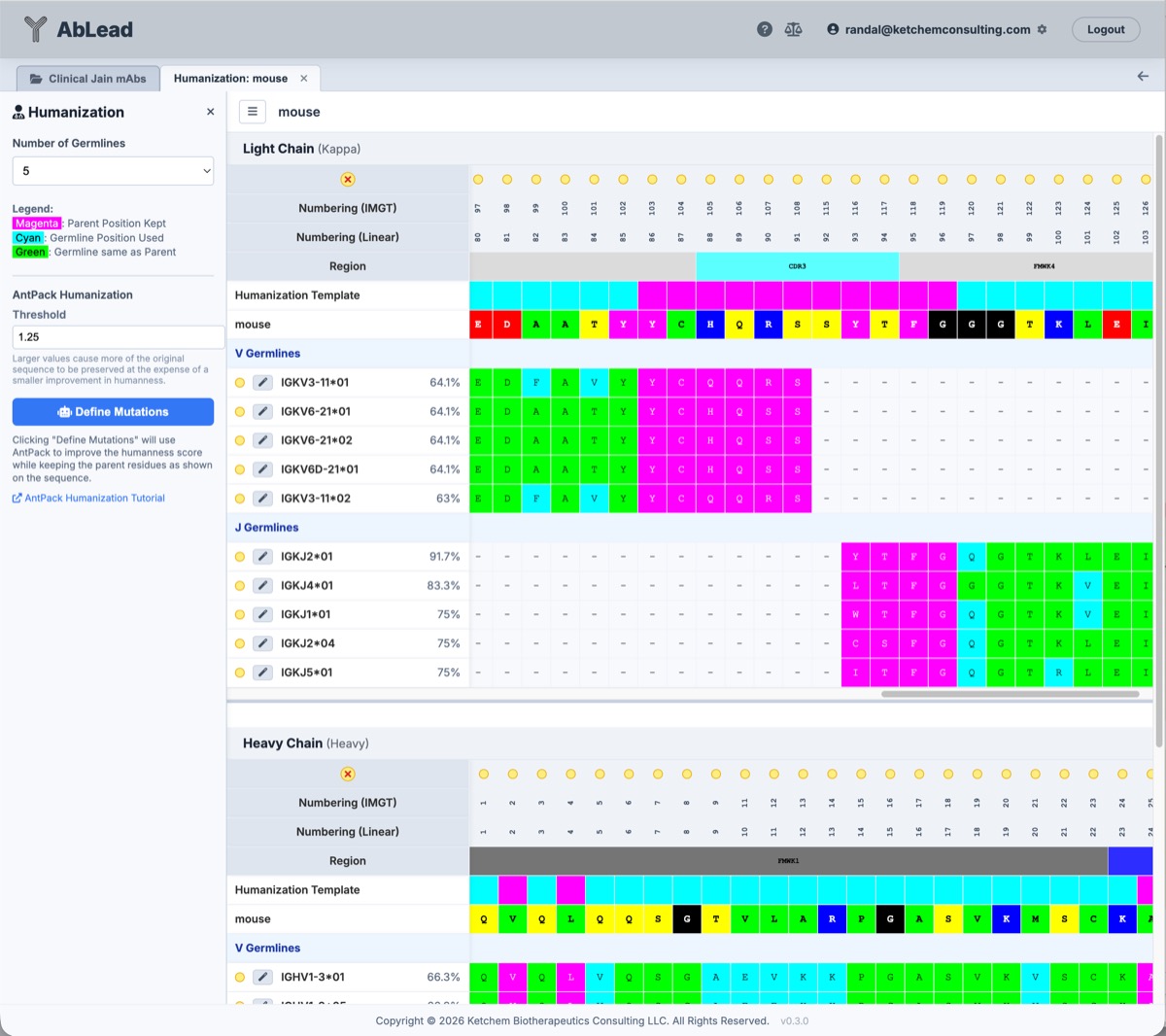
- Number of Germlines: Set the maximum number of germlines to view for potential humanization.
- Germline Selection: For each of the Light Chain and Heavy Chain V and J regions, select the desired germline using the wand icon to the left of the germline name. This will populate the Engineering mutation sets with the germline residues which are in the mutation template regions and which are different from the parent antibody.
- AntPack Humanization: An alternate method to germline picking is to let AntPack humanize the antibody. This is done by selecting the AntPack Define Mutations button. This will populate the Engineering mutation set with AntPack-defined mutations to optimize the humanness score while not mutating the Parent Position set as shown in Humanization Template. See the reference below for more details.
- Threshold: Default is 1.25. Larger values cause more of the original sequence to be preserved at the expense of a smaller improvement in humanness.
- Exclusions:
- Standard uses the same mask as the germline method.
- CDRs masks the currently defined CDR residues
- Selected excludes the residues selected by the column highlighter. Clicking "Select Std." will select the residues in the mutation template regions.
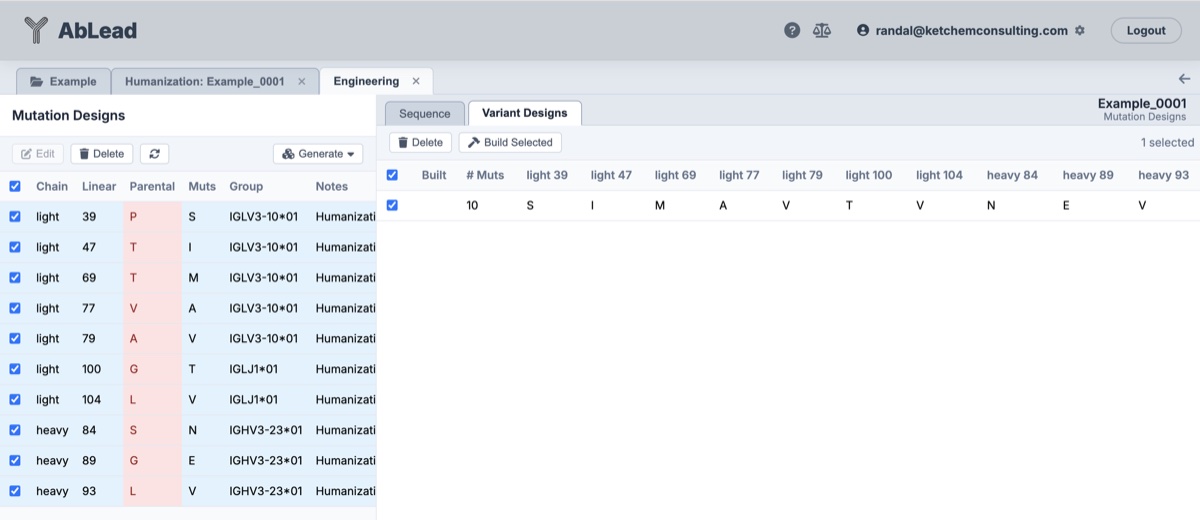
- Build New Antibodies: After defining the mutations, go to the Engineering tool Mutation design may be edited at this point to optimize the humanization design. Once the final design is entered, select the Mutation Designs, Generate Combinations, select the Variant Design, and Build Selected. The newly built antibody is a humanized version of the parent antibody.
References
- The germline template regions are described in Honegger, a. “Engineering Antibodies for Stability and Efficient Folding.” Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology, no. 181 (January 2008): 47–68.
- AntPack humanization is described in AntPack Humanization Tutorial.